Research Framework
Mathematical Foundations
The Interstella project leverages differential geometry and random dynamical systems to model semantic traversals in LLMs, drawing parallels to navigating black holes and wormholes in Interstellar.
Interstellar Analogy: Semantic Black Holes
Just as black holes warp spacetime, high-uncertainty regions in token embeddings act as "semantic black holes" – traversals must escape local minima to reach emergent insights.
Definitions
- Semantic Space: The manifold \( M \) of token embeddings, equipped with the Fisher information metric. Think of it as the curved fabric of the Token Cosmos.
- Traversal Path: A geodesic \( \gamma: [0,1] \to M \) connecting known to emergent regions, akin to plotting a course through a wormhole.
Theorems
Hopf-Rinow Theorem: In a complete Riemannian manifold, geodesic completeness implies compactness of closed balls, ensuring traversable paths in the semantic cosmos.
\[ d(p, q) < \infty \implies \text{existence of minimizing geodesic} \]Freidlin-Wentzell Large Deviations: For stochastic processes, the probability of rare events like AHA moments – the "Move 37" leaps in AlphaGo terms.
\[ \mathbb{P}(\tau_A < t) \approx \exp\left( - \inf_{\phi \in \mathcal{A}} I(\phi) \right) \] where \( I(\phi) \) is the rate function for rare traversals.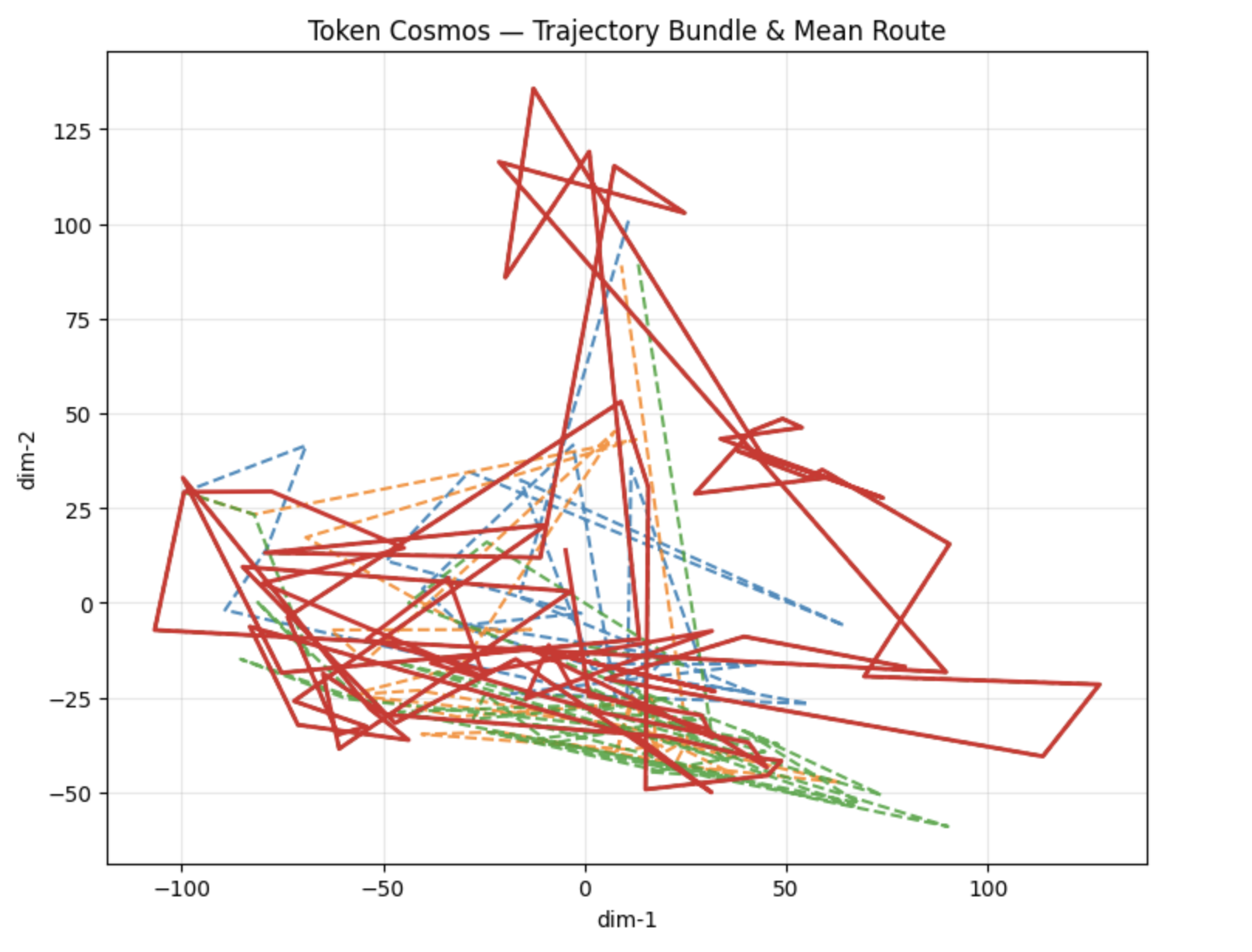
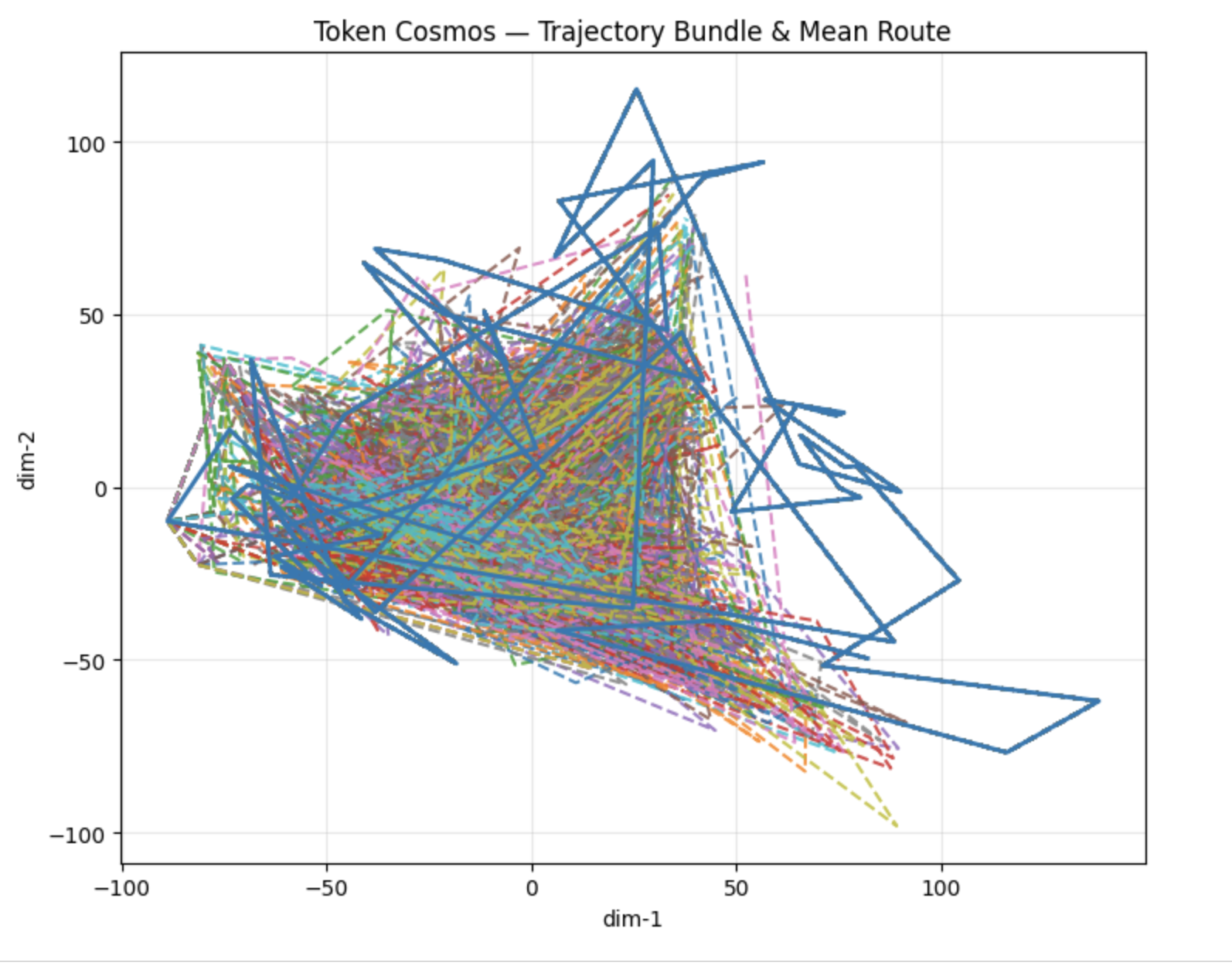
Geometric Model
Using Morse theory to identify critical points where topology changes, representing leaps to AGI capabilities – like emerging from a tesseract.
Interstellar Analogy: Wormholes as Attention
Attention mechanisms serve as wormholes, shortcutting vast semantic distances to connect distant ideas instantaneously.
The Fisher metric induces a geometry on the parameter space:
\[ ds^2 = g_{ij} d\theta^i d\theta^j \]Vector fields guide traversals through uncertainty landscapes, with gradients pointing toward higher-probability insights.
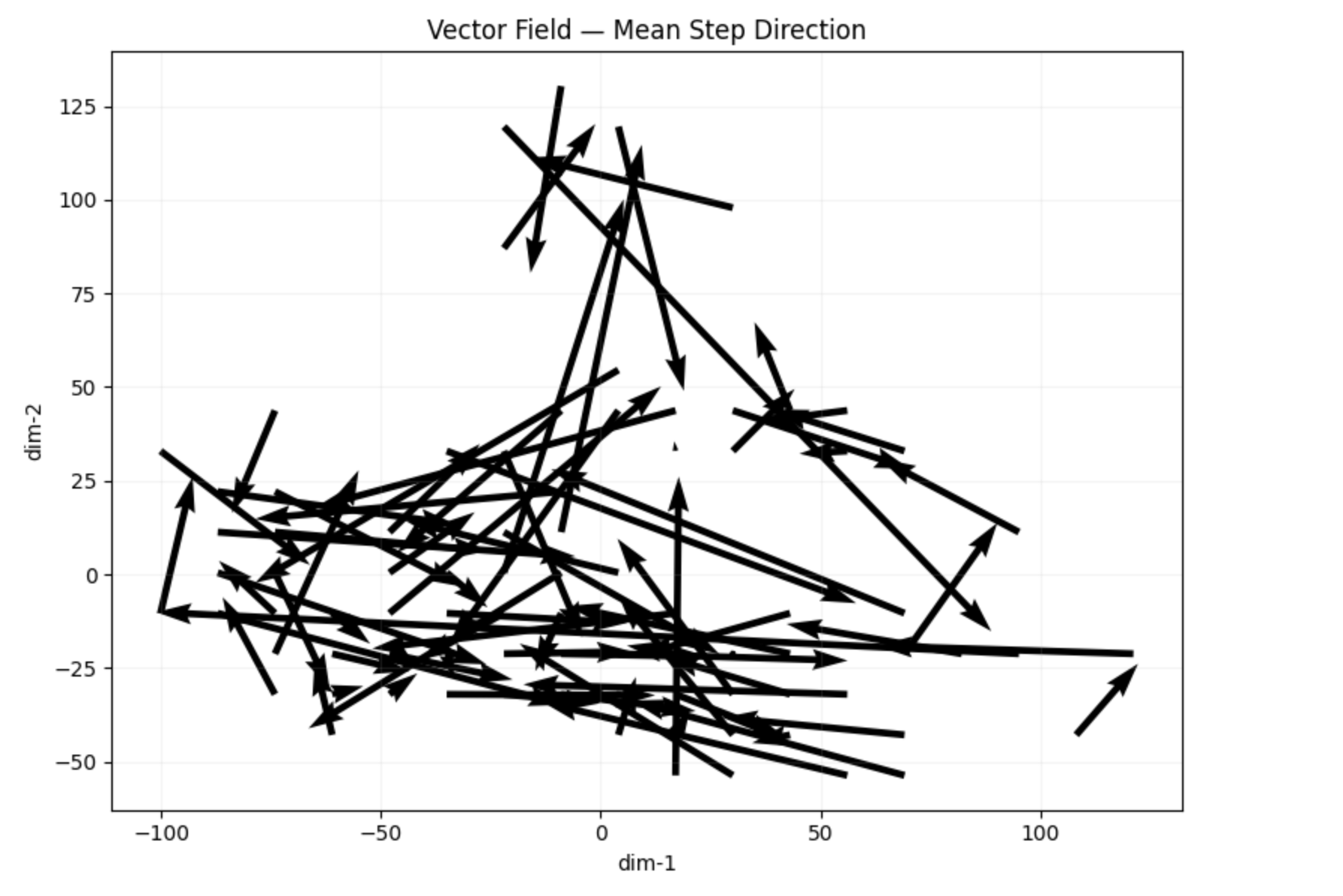
Probabilistic Reachability
Modeling token trajectories as random dynamical systems, with uncertainty quantified via entropy – the chaos of the unknown cosmos.
Reachability sets defined by:
\[ \mathcal{R}(x, t) = \{ y \in M \mid \exists \text{ path from } x \text{ to } y \text{ in time } t \} \]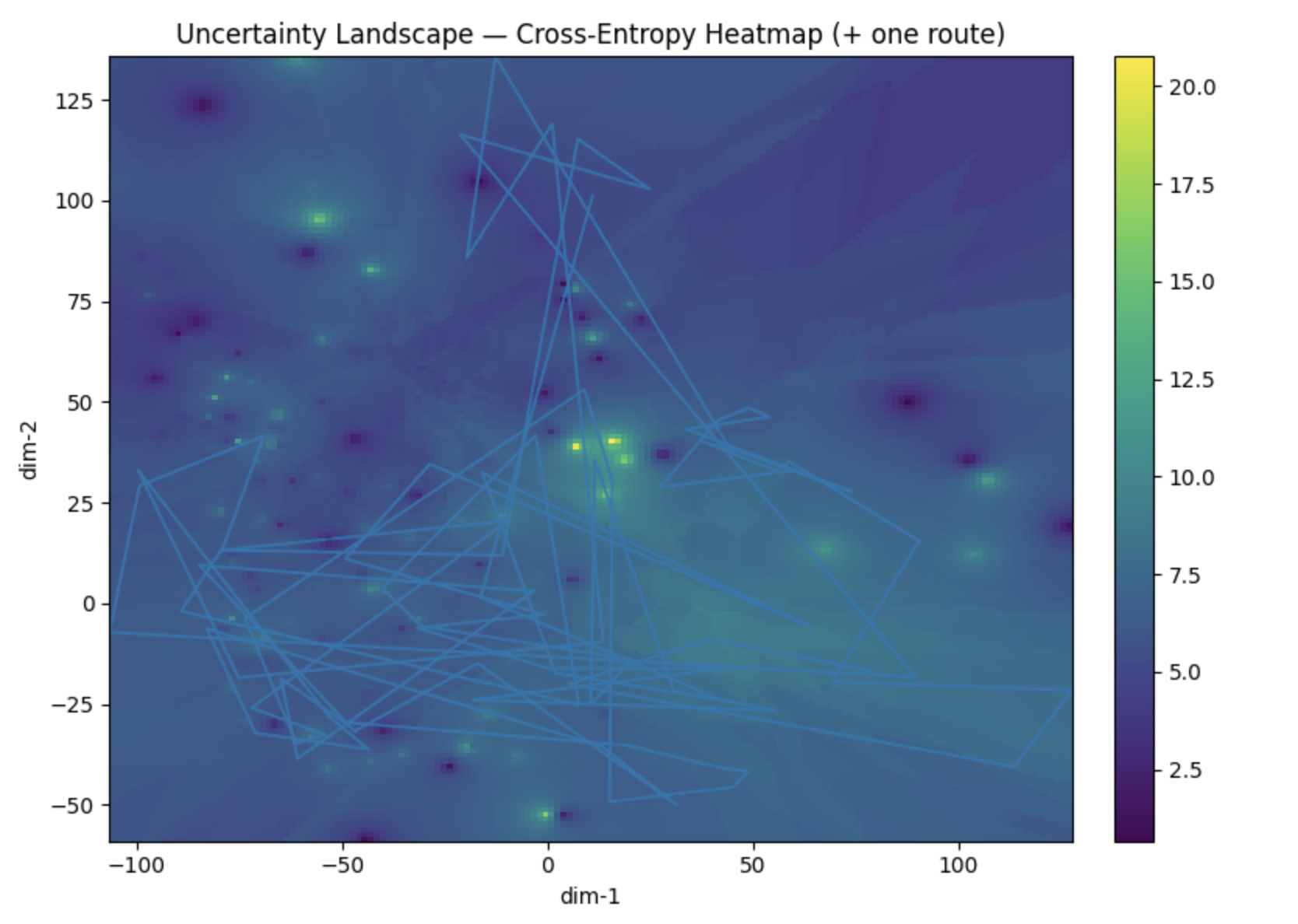
Discrete-Continuous Bridge
Bridging discrete token sequences to continuous manifold traversals using embedding layers and ODE solvers – from quantum bits to relativistic paths.
Example: Neural ODE for trajectory generation, simulating smooth journeys through discrete token jumps.
Engineered Pipeline
Layer 1: Navigator
Plans high-level traversal goals based on semantic queries, charting the course through the Token Cosmos.
Layer 2: Trajectory Generator
Generates candidate paths using geometric optimization, probing wormhole-like shortcuts.
Layer 3: Verifier
Checks reachability and safety in the token cosmos, avoiding event horizons of hallucinations.
Layer 4: Semantic Map
Updates the manifold map with new insights, charting discovered galaxies of knowledge.
Layer 5: Learning Loop
Refines the model through reinforcement from AHA detections, evolving toward autonomous AGI.